CBSE Class 12 Solutions MCQs:
Here are some MCQs from Solution chapter of class 12 chemistry. Lets dive into it.
Q-1: In which mode of expression, the concentration of a solution remains independent of temperature?
(a)Molarity
(b) Normality
(c) Formality
(d)Molality
Q-2: If 5.85g 0f NaCl is dissolved in 90g of water, the mole fraction of solute is:
(a)0.0196
(b)0.01
(c)0.1
(d)0.2
Q-3:Molarity is expressed as:
(a)mol/litre
(b)g/litre
(c)litre/mol
(d)mol/kg
Q-4:The number of moles of solute per kg of solvent is called:
(a)Molarity
(b) Normality
(c) Formality
(d)Molality
Q-5:Which of the following will form an ideal solution?
(a)Ethanol & water
(b)Nitric Acid & water
(c)Chloroform & Acetone
(d)Benzene & Toluene
Q-6:The mass of solute is expressed as 116ppm.What is its mass percentage?
(a)11.6
(b)0.116
(c)1.16
(d)0.0116
Q-7: If 18g of glucose is present in 1000g of solvent, the solution is said to be:
(a)1molar
(b)0.1molar
(c) 0.1molal
(d)0.5molal
Q-8: The colligative properties of a dilute solution depend upon:
(a)nature of solute
(b)nature of solvent
(c)no.of solute particles
(d)no.of solvent particles.
Q-9: Which of the following shows a negative deviation from Raoult’s law?
(a)Chloroform & Acetone
(b) Benzene & Ethanol
(c) Benzene & Toluene
(d) Benzene & carbon tetrachloride
Q-10: Which of the following shows a negative deviation from Raoult’s law?
(a)Chloroform & Acetone
(b) Benzene & Ethanol
(c) Benzene & Toluene
(d) Benzene & carbon tetrachloride
Q-11: At 250C,the highest osmotic pressure is exhibited by 0.1M solution of:
(a)CaCl2
(b)KCl
(c) NaCl
(d) MgSO4
CBSE Class 12 Solutions MCQs: Get more questions ahead
Q-12: Semipermeable membrane is that which permits the passage of:
(a)only solutes
(b)only solvents
(c)both solutes and solvents
(d)neither solutes nor solvents
Q-13:Which of the following units is useful in relating concentration of solution with its vapour pressure?
(a)mole fraction
(b) parts per million
(c) mass percentage
(d) molality
Q-14: On dissolving sugar in water at room temperature solution feels cool to touch.
Under which of the following cases dissolution of sugar will be most rapid?
(a) Sugar crystals in cold water.
(b) Sugar crystals in hot water.
(c) Powdered sugar in cold water.
(d) Powdered sugar in hot water.
Q-15:Maximum amount of a solid solute that can be dissolved in a specified amount of a given
liquid solvent does not depend upon:
(a) Temperature
(b) Nature of solute
(c) Pressure
(d) Nature of solvent
Q-16: A beaker contains a solution of substance ‘A’. Precipitation of substance ‘A’ takes place when small amount of ‘A’ is added to the solution. The solution is:
(a) saturated
(b) supersaturated
(c) unsaturated
(d) concentrated
Q-17: At equilibrium the rate of dissolution of a solid solute in a volatile liquid solvent is:
(a) less than the rate of crystallisation
(b) greater than the rate of crystallisation
(c) equal to the rate of crystallisation
(d) zero
Q-18: Which of the following aqueous solutions should have the highest boiling point?
(a) 1.0 M NaOH
(b) 1.0 M Na2SO4
(c) 1.0 M NH4NO3
(d) 1.0 M KNO3
Q-19: Considering the formation, breaking and strength of hydrogen bond, predict which of the
following mixtures will show a positive deviation from Raoult’s law?
(a) Methanol and acetone.
(b) Chloroform and acetone.
(c) Nitric acid and water.
(d) Phenol and aniline.
Q-20: Low concentration of oxygen in the blood and tissues of people living at high altitude is due to:
(a) low temperature
(b) low atmospheric pressure
(c) high atmospheric pressure
(d) both low temperature and high atmospheric pressure
Also Read: CBSE Class 12 Chemical Kinetics MCQs
Q-21: The values of Van’t Hoff factors for KCl, NaCl and K2 SO4 respectively are:
(a) 2, 2 and 2
(b) 2, 2 and 3
(c) 1, 1 and 2
(d) 1, 1 and 1
Q-22: Which of the following statements is false?
(a) Two different solutions of sucrose of same molality prepared in different solvents will have the
same depression in freezing point.
(b) The osmotic pressure of a solution is given by the equation Π = CRT ( where C is the molarity of
the solution).
(c) Decreasing order of osmotic pressure for 0.01 M aqueous solutions of barium chloride,
potassium chloride, acetic acid and sucrose is BaCl2 > KCl > CH3COOH > sucrose.
(d) According to Raoult’s law, the vapour pressure exerted by a volatile component of a solution is
directly proportional to its mole fraction in the solution.
Q-23: In comparison to a 0.01 M solution of glucose, the depression in freezing point of a 0.01 M
MgCl2 solution is:
(a) the same
(b) about twice
(c) about three times
(d) about six times
Q-24: At a given temperature, osmotic pressure of a concentrated solution of a substance .
(a) is higher than that at a dilute solution.
(b) is lower than that of a dilute solution.
(c) is same as that of a dilute solution.
(d) cannot be compared with osmotic pressure of dilute solution.
Q-25: The unit of ebulioscopic constant is:
(i) K kg mol–1 or K (molality)–1
(ii) mol kg K–1 or K–1(molality)
(iii) kg mol–1 K–1 or K–1(molality)–1
(iv) K mol kg–1 or K (molality)
Click here to Download the CBSE Provided Chemistry sample paper
Q-25: Which of the following statements is false?
(a) Units of atmospheric pressure and osmotic pressure are the same.
(b) In reverse osmosis, solvent molecules move through a semipermeable membrane from a
region of lower concentration of solute to a region of higher concentration.
(c) The value of molal depression constant depends on nature of solvent.
(d) Relative lowering of vapour pressure, is a dimensionless quantity.
Q-26: Value of Henry’s constant KH
(a) increases with increase in temperature.
(b) decreases with increase in temperature.
(c) remains constant.
(d) first increases then decreases.
Q-27: Isotonic solutions must have the same
a) solvent
b) density
c) concentration
d) depression in freezing point
Q-28: Which of the following binary mixtures will have same composition in liquid and vapour phase?
a) Benzene – Toluene
b) Water-Nitric acid
c) Water-Ethanol
d) n-Hexane – n-Heptane
Q-29: The value of Henry’s constant KH is
(a) greater for gases with higher solubility.
(b) greater for gases with lower solubility.
(c) constant for all gases.
(d) not related to the solubility of gases.
Q-30: Colligative properties are observed when
(a) a non volatile solid is dissolved in a volatile liquid.
(b) a non volatile liquid is dissolved in another volatile liquid.
(c) a gas is dissolved in non volatile liquid.
(d) a volatile liquid is dissolved in another volatile
Q-31:In isotonic solutions
(a) solute and solvent both are same.
(b) osmotic pressure is same.
(c) solute and solvent may or may not be same.
(d) solute is always same solvent may be different
Q-32: KH value for Ar(g), CO2 (g), HCHO (g) and CH4 (g) are 40.39, 1.67, 1.83×10–5 and 0.413
respectively.Arrange these gases in the order of their increasing solubility.
(a) HCHO < CH4 < CO2 < Ar
(b) HCHO < CO2 < CH4 < Ar
(c) Ar < CO2 < CH4 < HCHO
(d) Ar < CH4 < CO2 < HCHO
Q-33: KH value for Ar(g), CO2 (g), HCHO (g) and CH4 (g) are 40.39, 1.67, 1.83×10–5 and 0.413
respectively. Arrange these gases in the order of their increasing solubility.
(a) HCHO < CH4 < CO2 < Ar
(b) HCHO < CO2 < CH4 < Ar
(c) Ar < CO2 < CH4 < HCHO
(d) Ar < CH4 < CO2 < HCHO
Q-34: 4L of 0.02 M aqueous solution of NaCl was diluted by adding one litre of water. The molality of
the resultant solution is .
(a)0.004
(b) 0.008
(c) 0.012
(d) 0.016
Q-35: If two liquids A and B form minimum boiling azeotrope at some specific composition then .
(a) A–B interactions are stronger than those between A–A or B–B.
(b) vapour pressure of solution increases because more number of molecules of liquids A and B
can escape from the solution.
(c) vapour pressure of solution decreases because less number of molecules of only one of the
liquids escape from the solution.
(d) A–B interactions are weaker than those between A–A or B–B.
Q-36: On the basis of information given below mark the correct option.
Information : On adding acetone to methanol some of the hydrogen bonds between methanol molecules break.
(a) At specific composition methanol-acetone mixture will form minimum boiling azeotrope and will show positive deviation from Raoult’s law.
(b) At specific composition methanol-acetone mixture forms maximum boiling azeotrope
and will show positive deviation from Raoult’s law.
(c) At specific composition methanol-acetone mixture will form minimum boiling
azeotrope and will show negative deviation from Raoult’s law.
(d) At specific composition methanol-acetone mixture will form maximum boiling
azeotrope and will show negative deviation from Raoult’s law.
Q-37: Van’t Hoff factor i is given by the expression.

Q-38: Two beakers of capacity 500 mL were taken. One of these beakers, labelled as “A”, was filled with
400 mL water whereas the beaker labelled “B” was filled with 400 mL of 2 M solution of NaCl. At
the same temperature both the beakers were placed in closed containers of same material and same capacity as shown in
Fig. 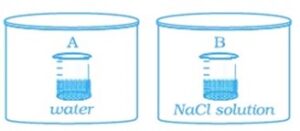
At a given temperature, which of the following statement is correct about the vapour pressure of pure water and that of NaCl solution.
(a) vapour pressure in container (A) is more than that in container (B).
(b) vapour pressure in container (A) is less than that in container (B).
(c) vapour pressure is equal in both the containers.
(d) vapour pressure in container (B) is twice the vapour pressure in container (A).
Q-39: For a binary ideal liquid solution, the variation in total vapour pressure versus composition
of solution is given by which of the curves?
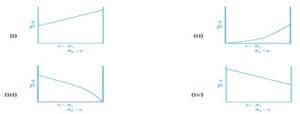
Q-40: Which of the following condition satisfies for ideal solution
(a)Change in volume is not equal to zero
(b)change in enthalpy is equal to zero
(c) Change in enthalpy is not equal to zero
(d) non of the above


Comments are closed.