CBSE Class 12 Chemical Kinetics MCQs: It will help to find some standard MCQs.
- The role of a catalyst is to change
(i) Gibbs energy of reaction.
(ii) enthalpy of reaction.
(iii) activation energy of reaction.
(iv) equilibrium constant.
- In the presence of a catalyst, the heat evolved or absorbed during the reaction
(i) increases.
(ii) decreases.
(iii) remains unchanged.
(iv) may increase or decrease.
- Activation energy of a chemical reaction can be determined by
(i) determining the rate constant at standard temperature.
(ii) determining the rate constants at two temperatures.
(iii) determining probability of collision.
(iv) using catalyst.
- Consider Fig. and mark the correct option.
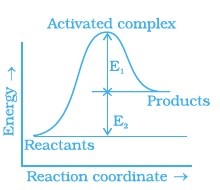
(i) Activation energy of forward reaction is E1 + E2 and product is less stable than reactant.
(ii) Activation energy of forward reaction is E1 + E2 and product is more stable than reactant.
(iii) Activation energy of both forward and backward reaction is E1 + E2 and reactant is more stable than product.
(iv) Activation energy of backward reaction is E1 and product is more stable than reactant.
- Consider a first order gas phase decomposition reaction given below :A(g) → B(g) + C(g)
The initial pressure of the system before decomposition of A was pi. After lapse of time ‘t’, total pressure of the system increased by x units and became ‘pt’ The rate constant k for the reaction is given as.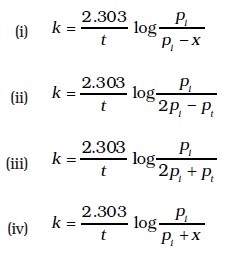
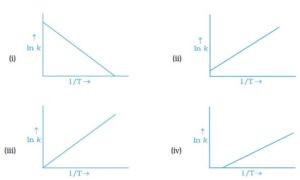
6. According to Arrhenius equation rate constant k is equal to Ae-Ea/RT . Which of the following represents the graph of ln k vs 1/T
vs 1/T
7.Consider the Arrhenius equation given below and mark the correct option. Ae-Ea/RT
(i) Rate constant increases exponentially with increasing activation energy and decreasing temperature.
(ii) Rate constant decreases exponentially with increasing activation energy and decreasing temperature.
(iii) Rate constant increases exponentially with decreasing activation energy and decreasing temperature.
(iv) Rate constant increases exponentially with decreasing activation energy and increasing temperature.
Also Read: CBSE Class 12 Electrochemistry MCQs
CBSE Class 12 Chemical Kinetics MCQs: It will help to find some standard MCQs.
- A graph of volume of hydrogen released vs time for the reaction between zinc and dil.HCl is given in Fig. On the basis of this mark the correct option.

Click Here To download the complete/ chapter wise e-book of NCERT Chemistry
9. Which of the following statements is not correct about order of a reaction.
(i) The order of a reaction can be a fractional number.
(ii) Order of a reaction is experimentally determined quantity.
(iii) The order of a reaction is always equal to the sum of the stoichiometric coefficients of reactants in the balanced chemical equation for a reaction.
(iv) The order of a reaction is the sum of the powers of molar concentration of the reactants in the rate law expression.
- Consider the graph given in Fig. Which of the following options does not show instantaneous rate of reaction at 40th second?
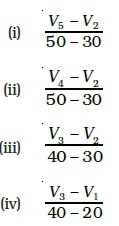
11. Which of the following statements is correct?
(i) The rate of a reaction decreases with passage of time as the concentration of reactants dereases.
(ii) The rate of a reaction is same at any time during the reaction.
(iii) The rate of a reaction is independent of temperature change.
(iv) The rate of a reaction decreases with increase in concentration of reactant(s).

12. Rate law for the reaction A + 2B → C is found to be
Rate = k [A][B]
Concentration of reactant ‘B’ is doubled, keeping the concentration of ‘A’ constant, the value of rate constant will be______.
(i) the same
(ii) doubled
(iii) quadrupled
(iv) halved
13. Which of the following statements is incorrect about the collison theory of chemical reaction?
(i) It considers reacting molecules or atoms to be hard spheres and ignores their structural features.
(ii) Number of effective collisions determines the rate of reaction.
(iii) Collision of atoms or molecules possessing sufficient threshold energy results into the product formation.
(iv) Molecules should collide with sufficient threshold energy and proper orientation for the collision to be effective.
14. A first order reaction is 50% completed in 1.26 × 1014 How much time would it take for 100% completion?
(i) 1.26 × 1015 s
(ii) 2.52 × 1014 s
(iii) 2.52 × 1028 s
(iv) infinite
15.Compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’ react according to the following chemical equation.
A (g) + 2 B (g) → 2C (g)
Concentration of either ‘A’ or ‘B’ were changed keeping the concentrations of one of the reactants constant and rates were measured as a function of initial concentration. Following results were obtained. Choose the correct option for the rate equations for this reaction.
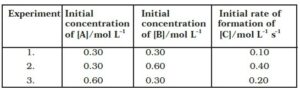
(i) Rate = k [A]2 [B]
(ii) Rate = k [A] [B]2
(iii) Rate = k [A] [B]
(iv) Rate = k [A]2 [B]0
16. Which of the following statement is not correct for the catalyst?
(i) It catalyses the forward and backward reaction to the same extent.
(ii) It alters ΔG of the reaction.
(iii) It is a substance that does not change the equilibrium constant of a reaction.
(iv) It provides an alternate mechanism by reducing activation energy between reactants and products.
17. The value of rate constant of a pseudo first order reaction ____________.
(i) depends on the concentration of reactants present in small amount.
(ii) depends on the concentration of reactants present in excess.
(iii) is independent of the concentration of reactants.
(iv) depends only on temperature.
18. Consider the reaction A & B. The concentration of both the reactants and the products varies exponentially with time. Which of the following figures correctly describes the change in concentration of reactants and products with time?
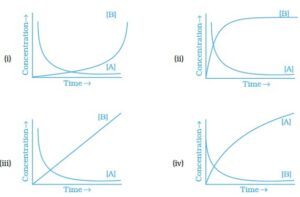
19. Rate law cannot be determined from balanced chemical equation if _______.
(i) reverse reaction is involved.
(ii) it is an elementary reaction.
(iii) it is a sequence of elementary reactions.
(iv) any of the reactants is in excess.
20. Which of the following statements are applicable to a balanced chemical equation of an elementary reaction?
(i) Order is same as molecularity.
(ii) Order is less than the molecularity.
(iii) Order is greater than the molecularity.
(iv) Molecularity can never be zero.
21. In any unimolecular reaction ______________.
(i) only one reacting species is involved in the rate determining step.
(ii) the order and the molecularity of slowest step are equal to one.
(iii) the molecularity of the reaction is one and order is zero.
(iv) both molecularity and order of the reaction are one.
22. For a complex reaction ______________.
(i) order of overall reaction is same as molecularity of the slowest step.
(ii) order of overall reaction is less than the molecularity of the slowest step.
(iii) order of overall reaction is greater than molecularity of the slowest step.
(iv) molecularity of the slowest step is never zero or non interger.23..A plot of log(a-x) against ‘t’ is a straight line. This indicates that the reaction is of:
(i)zero order (ii)first order (iii)second order (iv)third order
23..The rate of reaction between A & B increases by a factor of 100,when the concentration of A
is increased 10 folds.The order of reaction with respect to A is:
(i)10 (ii)2 (iii)1 (iv)20
24. The rate of reaction, A + B Products,is given by the rate law, r =k[A][B].If B is taken as
large excess,the order of reaction is:
(i)2 (ii)Zero (iii)1 (iv)unpredictable
25 .Which plot can give us the value of activation energy?
(i) k versus T (ii) 1/k versus T (iii) logk versus 1/T (iv) C versus T
26. .The second order reaction is expressed as:
(i) mol L-1s-1 (ii) mol-1L-1s-1 (iii) mol-1Ls-1 (iv) molLs-1
27..For a zero order reaction:
(i)t1/2 α a (ii) t1/2 α 1/a (iii) t1/2 α a2 (iv) t1/2 α 1/a2
28. .For a reaction,the rate of reaction is quadrupled when the concentration of the reactant is doubled.what is the order of the reaction?
(i) 1 (ii) 0 (iii) 3 (iv) 2
29.At high pressure the following reaction is zero order.
Which of the following options are correct for this reaction?
(i) Rate of reaction = Rate constant
(ii) Rate of the reaction depends on concentration of ammonia.
(iii) Rate of decomposition of ammonia will remain constant until ammonia disappears completely.
(iv) Further increase in pressure will change the rate of reaction.
30.Which of the following statements are in accordance with the Arrhenius equation?
(i) Rate of a reaction increases with increase in temperature.
(ii) Rate of a reaction increases with decrease in activation energy.
(iii) Rate constant decreases exponentially with increase in temperature.
(iv) Rate of reaction decreases with decrease in activation energy.
Click here to Download the CBSE Provided Chemistry sample paper


Comments are closed.