Syllabuswise.com have curated a Chemistry Sample Paper Class 12 20203 based on the patterns Shared by CBSE 2023. For this Question set you can get Answers also at the end of the Sample paper, Even its download the pdf of the question paper. We have shared a pdf and word format file so that it will helpful for Our Teachers also.
Chemistry Sample Paper Class 12 2023
| General Instructions:
Read the following instructions carefully a. There are 35 questions in this question paper with internal choice. b. SECTION A consists of 18 multiple-choice questions carrying 1 mark each c. SECTION B consists of 7 very short answer questions carrying 2 marks each d. SECTION C consists of 5 short answer questions carrying 3 marks each e. SECTION D consists of 2 case- based questions carrying 4 marks each f. SECTION E consists of 3 long answer questions carrying 5 marks each
|
||
| Q.No |
Questions |
Marks |
|
SECTION-A The following questions are multiple choice questions with one correct answer. Each question carries 1 mark. There is no internal choice in this section. |
||
| 1 | Reactivity order of SN1 reaction for the following compounds is
|
1 |
| 2 | From the folowing alcohol which does not react with Lucas reagent is (a) isobutyl alcohol (b) n-butanol (c) tert-butyl alcohol (d) sec-butyl alcohol |
1 |
| 3 | Colour of transition metal ions are due to absorption of some wavelength. This results in
(a) d-s transition |
1 |
| 4 | Which of the following is given to a fuel cell’s cathode?
a) Hydrogen b) Nitrogen c) Oxygen d) Chlorine |
1 |
| 5 | The reaction rate constant can be defined as the rate of reaction when each reactant’s concentration is ___________.
a) Zero b) Unity c) Doubled the initial concentration d) Infinite |
1 |
| 6 | Consider the given figure and mark the correct option.
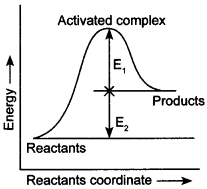 (а) Activation energy of forward reaction is E1 + E2 and product is less stable than reactant. |
1 |
| 7 | The correct order of increasing the reactivity of C—X bond towards nucleophile in following compounds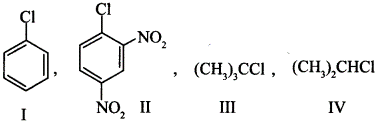 (a) IV < III < I < II (c) I < II < IV < III (b) III < II < I < IV (d) II < III < I < IV |
1 |
| 8 | Which reagents are required for one step conversion of chlorobenzene to toluene?
(a) CH3Cl / AlCl3 (b) CH3Cl, Na, Dry ether (c)CH3Cl/Fe dark (d) NaNO2/ HCl /0-50oC |
1 |
| 9 | Which of these statements about [Co(CN)6]3- is true? (a) It has 4 unpaired electron, high spin (b) No unpaired electron, high spin (c) No unpaired electron, low spin (d) 4 unpaired electron, low spin |
1 |
| 10 | By reacting with which of the following, primary amines can be separated from secondary and tertiary amines?
a) Chloroform alone b) Methyl iodide c) Chloroform and alcoholic KOH d) Zinc dust |
1 |
| 11 | The formation of cyanohydrin from a ketone is an example of (a) electrophilic addition (b) nucleophilic addition (c) nucleophilic substitution (d) electrophilic substitution |
1 |
| 12 | The activation energy of a reaction can be determined from the slope of which of the following graph:
|
1 |
| 13 | The reaction of ethyl formate with an excess of CH3MgI followed by hydrolysis gives (a) ethanol (b) n-propyl alcohol (c) propanal (d) isopropyl alcohol |
1 |
| 14 | Which of the following will not give test for Cl– with AgNO3(aq) at 25°C? (a) COCl3.5NH3 (b) COCl3.3NH3 (c) COCl3.6NH3 d) COCl3.4NH3 |
1 |
| Given below are two statements labelled as Assertion (A) and Reason (R)
|
||
| 15 | Assertion : In case of phenol, bromination takes place even in absence of Lewis acid whereas bromination of benzene takes place in presence of Lewis acid like FeBr3. Reason : – OH group attached to benzene ring is highly deactivating.Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:a. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of Ab. Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.c. A is true but R is false.d. A is false but R is true. |
1 |
| 16 | Assertion : In presence of enzyme, substrate molecule can be attacked by the reagent effectively. Reason : Active sites of enzymes hold the substrate molecule in a suitable position.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below: a. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A b. Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A. c. A is true but R is false. d. A is false but R is true. |
1 |
| 17 | Assertion : Cuprous ion (Cu+) has unpaired electrons while cupric ion (Cu++) does not. Reason : Cuprous ion (Cu+) is colourless whereas cupric ion (Cu++) is blue in the aqueous solution. Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:a. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of Ab. Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.c. A is true but R is false.d. A is false but R is true. |
1 |
| 18 | Assertion: Aquatic species are more comfortable in warm water rather than in cold water.
Reason: Different gasses have different KH values at the same temperature. Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below: a. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A b. Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A. c. A is true but R is false. d. A is false but R is true. |
1 |
Chemistry Sample Paper Class 12 2023SECTION-B |
||
| 19 | The rate constant of a reaction A → B is 0.6 × 103 mol S-1 . If the concentration of [A] is 5 M, then what will be concentration of [B] after 20 months? | 2 |
| 20 | a) Vitamin C cannot be stored in our body? Justify
b) What are reducing sugars? OR What happens when D-glucose is treated with the following reagents? a) HI b) Bromine Water |
2 |
| 21 | a)Why is f-butyl bromide more reactive towards SN1 reaction as compared to n-butyl bromide?
b)What is the major product formed from dehydrohalogenation of 2-Bromopentane? OR a) Out of o-and p-dibromobenzene which one has a higher melting point and why? b) Why is the solubility of haloalkanes in water very low? |
2 |
| 22 | On the basis of crystal field theory explains why Co (III) forms a paramagnetic octahedral complex with weak field ligands whereas it forms a diamagnetic octahedral complex with strong field ligands. Explain . | 2 |
| 23 | Value of standard electrode potential for the oxidation of Cl– ions is more positive than that of water, even then in the electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride, why are Cl– ions oxidised at anode instead of water ? | 2 |
| 24 | What is meant by pseudo first order reaction? Give an example and mention its rate law equation. | 2 |
| 25 | An aromatic compound “A” on heated with NaNO2+ HCl produces Benzene diazomium chloride, which on further treatment with Cu2Cl2 produces an molecule “B”. While B undergoes coupling reaction to produce biphenyl with an reagent C.
Mention A ,B & C and mention name of the coupling reaction occurred between B & C |
2 |
| SECTION-C | ||
| 26 | a)Write IUPAC name of the following :
b) Write the equations involved in Wolff-Kishner reduction. |
3 |
| 27 | (a)Why [Ni(CO)4] is more stable than [NiCl4]2- ?
(b)On the basis of CFT,write the electronic configuration of d5 ion if Δ0<P. (c)[Cr(NH3)6]3+ is paramagnetic but [Ni(CN)4]2- is diamagnetic. Explain why? |
3 |
| 28 | a)To lower the melting point of 75 g of acetic acid by 1.50C, how much mass of ascorbic acid is needed to be dissolved in the solution where Kt = 3.9 K kg mol-1
b) If 22 g of benzene is dissolved in 122 g of carbon tetrachloride, determine the mass percentage of carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) and benzene (C6H6). |
3 |
| 29 | What happens when : Answer any 3 of the followings.
(a)Aniline is treated with acetic anhydride followed by the reaction with Br2 in presence of acetic acid. (b)Benzenamine is treated with acetic andydride. (c) Arrange the following in decreasing order of their basic strength. C6H5NH2,C2H5NH2,(C2H5)2NH,NH3 (d) Aniline doesn’t react with methyl chloride in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3 catalyst. |
3 |
| 30 | a) Chloroform is stored in dark coloured bottles.
b)Mention the product formed.
|
3 |
|
Don’t forget to click the Class 12 solution chapter MCQs and Assertion & Reason Question Bank SECTION-D |
||
| 31 | Polysaccharides may be very large molecules. Starch, glycogen, cellulose, and chitin are examples of polysaccharides. Starch is the stored form of sugars in plants and is made up of amylose and amylopectin (both polymers of glucose). Amylose is soluble in water and can be hydrolyzed into glucose units breaking glycocidic bonds, by the enzymes α- amylase and β-amylase. It is straight chain polymer.
Amylopectin is a branched chain polymer of several D-glucose molecules. 80% of amylopectin is present in starch. Plants are able to synthesize glucose, and the excess glucose is stored as starch in different plant parts, including roots and seeds. The starch that is consumed by animals is broken down into smaller molecules, such as glucose. The cells can then absorb the glucose. Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in humans and other vertebrates, and is made up of monomers of glucose. It is structurally quite similar to amylopectin . Glycogen is the animal equivalent of starch. It is stored in liver and skeletal muscles. Cellulose is one of the most abundant natural biopolymers. The cell walls of plants are mostly made of cellulose, which provides structural support to the cell. Wood and paper are mostly cellulosic in nature. Like amylose, cellulose is a linear polymer of glucose. Cellulose is made up of glucose monomers that are linked by bonds between particular carbon atoms in the glucose molecule. Every other glucose monomer in cellulose is flipped over and packed tightly as extended long chains making high tensile. Answer the Followings a) Cellulose on complete hydrolysis yields: i. amylose ii. amylopectin iii. glucose iv. amylose and amylopectin b) a) The linkages which join monosaccharides to form long chain polysaccharides is? c) What are essential and non-essential amino acids? Give two examples of each. OR d) What is meant by Monosaccharides and ‘reducing sugars’? |
4 |
| 32 | Boiling point or freezing point of liquid solution would be affected by the dissolved solids in the liquid phase. A soluble solid in solution has the effect of raising its boiling point and depressing its freezing point. The addition of non-volatile substances to a solvent decreases the vapor pressure and the added solute particles affect the formation of pure solvent crystals.
According to many researches the decrease in freezing point directly correlated to the concentration of solutes dissolved in the solvent. This phenomenon is expressed as freezing point depression and it is useful for several applications such as freeze concentration of liquid food and to find the molar mass of an unknown solute in the solution. Freeze concentration is a high quality liquid food concentration method where water is removed by forming ice crystals. This is done by cooling the liquid food below the freezing point of the solution. The freezing point depression is referred as a colligative property and it is proportional to the molar concentration of the solution (m), along with vapor pressure lowering, boiling point elevation, and osmotic pressure. These are physical characteristics of solutions that depend only on the identity of the solvent and the concentration of the solute. The characters are not depending on the solute’s identity .Freezing point depression of different Sucrose solutions and coconut water.) a. When a non volatile solid is added to pure water it will: (Chose Correct One) i. boil above 100oC and freeze above 0oC ii. boil below 100oC and freeze above 0oC iii. boil above 100oC and freeze below 0oC iv. boil below 100oC and freeze below 0oC b. Define Colligative Property. c. Assume three samples of juices A, B and C have glucose as the only sugar present in them. The concentration of sample A, B and C are 0.1M,0.5M and 0.2 M respectively. Which solution will have highest Boiling Point an why? OR d) Among all Colligative properties which colligative property don’t change with Change in Temperature and explain why? |
4 |
| SECTION-E | ||
| 33 | Define the following terms : (i) Limiting molar conductivity(ii) Fuel cell(b) For the cell reaction Ni(s) | Ni2+(aq) || Ag+(aq) | Ag(s) Calculate the equilibrium constant at 25 °C. How much maximum work would be obtained by operation of this cell? EoNi2/Ni = 0.25 V and EoAg+/Ag = 0.80 V.ORa) Define conductivity and molar conductivity for the solution of an electrolyte. Discuss their variation with concentration. (b) Calculate the standard cell potential of the galvanic cell in which the following reaction takes place : Fe2+ (aq) + Ag+ (aq) → Fe3+ (aq) + Ag (s) Calculate the ΔrG° and equilibrium constant of the reaction also. (E0Ag+/Ag = 0.80 V; E0Fe3+/Fe2+ = 0.77 V) |
5 |
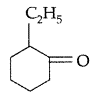
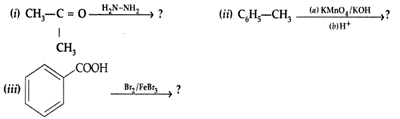
| 34 | a)Predict the products of the following reactions :
b) Do the following conversions in not more than two steps: Or (a) Write chemical equations to illustrate the following name bearing reactions : c) Convert Ethanol to 3-hydroxybutanal |
5 |
| 35 | Explain the following observations : (a) Generally there is an increase in density of elements from titanium (Z = 22) to copper (Z = 29) in the first series of transition elements. (b) Transition elements and their compounds are generally found to be good catalysts in chemical reactions.(c)The chemistry of actinoids is not so smooth as that of lanthanoids(d) The ionization enthalpies (first and second) in the first series of the transition elements are found to vary irregularly.(e) Represent the oxidising action of potassium dichromate and write the ionic equations for its reaction with iodine. |
5 |
Click here to download Chemistry Sample Paper Class 12 2023 MS word File
Click here to download Chemistry Sample Paper Class 12 2023 pdf File
Click here to download the Answer key of the this Sample Paper
Don’t forget to click the Class 12 solution chapter MCQs and Assertion & Reason Question Bank

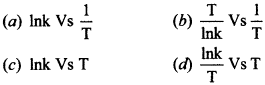
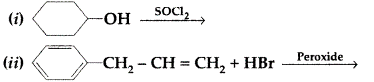
Comments are closed.